有一天,电子和正电子相爱了……
7
2011
生成 Awesome 的“应用程序”菜单
Ubuntu 下,Awesome 有个叫 debian_menu 的模块,用于向 Awesome 菜单中添加一个类似于 GNOME 的“应用程序”菜单的项。然而到了 ArchLinux 下,却没这么个模块了。本来我并不太在意,但看到别人折腾后,自己又开始手痒了。
本来是准备自己用 Python 写个程序来生成的,用 pkgfile 一查,却发现有archlinux-xdg-menu这么个软件包,遂装了。原来主要是两个 Perl 脚本。其一生成各种格式的菜单配置,其二根据配置文件为指定的窗口管理器生成菜单配置文件。虽然看示例配置文件似乎不支持 Awesome,但xdg_menu --help一看却是支持 Awesome 的。
xdg_menu --format awesome > ~/.config/awesome/menu.lua
然后改下rc.lua,把这个大菜单加上就可以了:
require("menu")
mymainmenu = awful.menu({ items = { { "Awesome", myawesomemenu, beautiful.awesome_icon },
-- ...
{ "应用程序 (&A)", xdgmenu },
-- ...
截图如下:
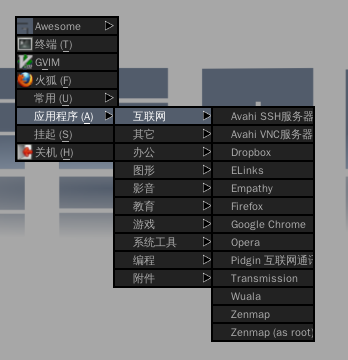
效果不错,只可惜没图标。
又:从 wiki 上看到,原来这菜单可以添加快捷键的,只要在相应字母前加上&符号即可。
2011年12月3日更新:dlin帮忙修改了archlinux-xdg-menu,现在有图标了 ;-)
2012年5月28日更新:现在 Arch 下需要稍微修改下命令参数了:
xdg_menu --format awesome --root-menu /etc/xdg/menus/arch-applications.menu > ~/.config/awesome/menu.lua
7
2011
Awesome 中 GIMP 窗口的处理
GIMP一启动就有三个窗口,一个显示图像的,一个工具箱,一个图层什么的。工具箱和图层这些虽然被Awesome自动判为浮动窗口了,但因为显示图像的主窗口是最大化,所以它们经常被图像窗口遮住。将这两个窗口置顶是最简单的办法,但是不太完美。这样它们也会遮住诸如我的浮动终端之类的窗口。
既然是高可配置的Awesome,当然不是没有办法让它们乖乖听话。于是翻翻手册,在我的 rc.lua 里又加了如下代码:
-- {{{2 for GIMP
client.add_signal("focus", function(c)
if c.class and c.class == 'Gimp-2.6' then
for _, i in ipairs(c:tags()) do
for _, j in ipairs(i:clients()) do
if j.role and (j.role == 'gimp-toolbox' or j.role == 'gimp-dock') then
j.above = true
end
end
end
end
end)
client.add_signal("unfocus", function(c)
if c.class and c.class == 'Gimp-2.6' then
for _, i in ipairs(c:tags()) do
for _, j in ipairs(i:clients()) do
if j.role and (j.role == 'gimp-toolbox' or j.role == 'gimp-dock') then
j.above = false
end
end
end
end
end)
这样在 GIMP 的窗口获得焦点时就把那两个窗口置顶,失去焦点时再取消置顶。不过令我有些不解的是,不能给单个的client对象添加信号处理。
24
2011
改变终端下的光标颜色,包括 screen 和 tmux!
曾经在Ubuntu中文论坛里看到一个改变光标颜色的方法,用光标颜色来指示是在 Vim 的普通模式还是插入模式下(因为 gnome-terminal 不支持使用转义序列改变光标形状)。Vim Wiki 上的 tip。
if &term =~ "xterm\|rxvt" silent !echo -ne "\e]12;HotPink\007" let &t_SI="\e]12;RoyalBlue1\007" let &t_EI="\e]12;HotPink\007" autocmd VimLeave * :!echo -ne "\e]12;green\007" endif
可惜它不适用于当时我正在使用的 screen。现在我改用 tmux 了,偶然改变TERM变量测试的时候,发现光标颜色竟然改变了——虽然还附带一些“不良反应”。我想到:一定有办法来正确地改变光标颜色的!
于是求助于 Google,很快找到了这个,有了用于 screen 的转义序列。不过依旧不适用于 tmux。把“tmux”也加到关键词里再搜,终于找到了这个。根据这个帖子,screen 和 tmux 比 xterm 多出来的那些字符序列是告诉 screen 或者 tmux 把其中的字符序列直接发送到终端模拟器处理。
于是,我的 vimrc 又可以更新了:
let color_normal = 'HotPink'
let color_insert = 'RoyalBlue1'
let color_exit = 'green'
if &term =~ 'xterm\|rxvt'
exe 'silent !echo -ne "\e]12;"' . shellescape(color_normal, 1) . '"\007"'
let &t_SI="\e]12;" . color_insert . "\007"
let &t_EI="\e]12;" . color_normal . "\007"
exe 'autocmd VimLeave * :!echo -ne "\e]12;"' . shellescape(color_exit, 1) . '"\007"'
elseif &term =~ "screen"
if !exists('$SUDO_UID')
if exists('$TMUX')
exe 'silent !echo -ne "\033Ptmux;\033\e]12;"' . shellescape(color_normal, 1) . '"\007\033\\"'
let &t_SI="\033Ptmux;\033\e]12;" . color_insert . "\007\033\\"
let &t_EI="\033Ptmux;\033\e]12;" . color_normal . "\007\033\\"
exe 'autocmd VimLeave * :!echo -ne "\033Ptmux;\033\e]12;"' . shellescape(color_exit, 1) . '"\007\033\\"'
else
exe 'silent !echo -ne "\033P\e]12;"' . shellescape(color_normal, 1) . '"\007\033\\"'
let &t_SI="\033P\e]12;" . color_insert . "\007\033\\"
let &t_EI="\033P\e]12;" . color_normal . "\007\033\\"
exe 'autocmd VimLeave * :!echo -ne "\033P\e]12;"' . shellescape(color_exit, 1) . '"\007\033\\"'
endif
endif
endif
unlet color_normal
unlet color_insert
unlet color_exit
因为 tmux 的TERM变量和 screen 的一致,所以得使用TMUX变量来判断是在 tmux 里还是在 screen 里。
最后,说下指定颜色的方法。可以使用和 HTML 中一样的#rrggbb甚至简写#rgb,也可以使用颜色名。这里有个 xterm 的颜色名表。
2011年8月25日更新:
写了个 zsh 函数:
if [[ $TERM == xterm* ]] || [[ $TERM == *rxvt* ]]; then # {{{2 设置光标颜色
cursorcolor () { echo -ne "\e]12;$*\007" }
elif [[ $TERM == screen* ]]; then
if [[ -n "$TMUX" ]]; then
cursorcolor () { echo -ne "\ePtmux;\e\e]12;$*\007\e\\" }
else
cursorcolor () { echo -ne "\eP\e]12;$*\007\e\\" }
fi
fi
15
2011
userChrome 脚本:中键粘贴并搜索
Google 字典没了,但单词还是要查的。目前用的是沪江小D。实际上之前也一直在用它的划词查询书签。释义简单了点,但速度是足够快了。可是再也不能之前选中单词后点几下就能查到了(划词有时候会很烦,特别是与FireGuesture的搜索冲突的时候)。过了几天使用Ctrl-C来复制或者Ctrl-W来清除上一个词或者Ctrl-T打开新标签使用关键字搜索的日子,最终还是忍不住折腾了起来,最后终于写成以下脚本:
if(location == "chrome://browser/content/browser.xul"){
var s = document.getElementById('searchbar');
s.addEventListener('mousedown', function(e){
if(e.button == 1){
this.value = '';
}
return true;
}, false);
s.addEventListener('mouseup', function(e){
if(e.button == 1){
var where = e.altKey ? 'current' : 'tab';
}
setTimeout(function(){
if(s.value){
s.doSearch(s.value, where);
}
}, 100);
return true;
}, false);
}
使用方法:
先吐槽下:这使用方法可比脚本难找得多。我是边 Google 边摸索才弄明白的。
首先安装userChromeJS插件。火狐现在已经不再读取userChrome.js文件,所以需要这个插件。另外火狐5的话目前需要Add-on Compatibility Reporter这个插件。然后就是把代码粘贴到<firefox_profile>/chrome/userChrome.js文件里了。行家的话应该知道怎么单独文件之类的,我暂时就懒得研究了。
一切就绪后重启火狐。这时在搜索框点击鼠标中键就会将 X 剪贴板的内容粘贴到搜索框中并在新标签页中打开搜索。如果点击的时候按住Alt键的话,会在当时页面中打开。
最后,既然用到的 X 剪贴板,当然是不支持 Windows 了。(我还不会用Javascript操纵剪贴板。。。)
8
2011
再见了,Google 字典!
今天,当我又遇到一个不太认识的单词时,我像往常那样选中它,然后切换到火狐标签栏的第一个已固定的标签页,正准备连续在输入框点击左键和中键来查询的时候,蓦然发现,Google 字典不告而别了——
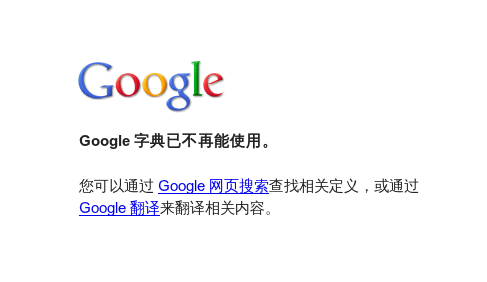
曾经有一次,Google 字典变成了 Google 搜索。当时我就很失落——这么好用的一个工具没了。第二天一看,它又回来了。我以为是用户的反对使 Google 反悔了。可是现在,即使明天它再回来,我也不敢再信任了。已经开了好几个月的固定标签页关掉吧,删除相关书签和搜索关键字。下个星期再去删未完成的抓取 Google 字典的 Python 脚本。至于那个我自己修改过的 GreaseMonkey 脚本,算了吧,留着作为纪念好了。
31
2011
在 ncurses 中使用 readline
有一天,我发现了一个很好用的 Python shell——bpython。它使用了 ncurses 来做界面,使用了 pygments 来高亮代码,怎么看都比 ipython 漂亮,更不用说 Python 自己的了。不过既然它使用了 ncurses,麻烦也就来了——ncurses 不支持 readline!虽然有些模拟,但终究是不好用,M-f M-b不起使用,M-数字也不能用。于是我再次去 google 同时使用 ncurses 和 readline 这两个库的办法。
功夫不负有心人,这次终于 google 到了点有用的东西:
The basic idea is to use call rl_callback_read_char() when input from the user is available (determined with select, or similar), then print 'rl_line_buffer' as you would any other string in ncurses, and optionally set A_REVERSE on the position indicated by rl_point. (or just reposition the cursor I guess, either works...)
不过可惜的是,这封邮件给出的代码在我这里并没有跑起来。其实跑起来了也用处不大,因为我需要的那部分代码独立性太差了,还是得重写。
花了一个下午,我终于弄出了一个雏形。
首先,这个rl_callback_read_char()是这么用的(文档):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<readline/readline.h>
int main(void){
int cont = 1;
void callback(char *text){
if(text == NULL){
rl_callback_handler_remove();
putchar('\n');
cont = 0;
}else{
printf("%s.\n", text);
}
}
rl_callback_handler_install(">> ", callback);
while(cont){
rl_callback_read_char();
}
return 0;
}
首先安装个回调函数,它将在 readline 读取到一行内容时调用。当标准输入可用的时候,调用rl_callback_read_char()来读取字符。另外注意,这里我用了 gcc 的嵌套函数支持,免得弄出不少全局变量。
知道怎么用rl_callback_read_char()之后,就可以按那封邮件所说的,把它和 ncurses 联合起来了。代码修改自NCURSES Programming HOWTO。思路很简单,readline 负责读取并处理用户输入,显示是自己处理的。不过作为中文用户,纠结了半天的中文问题。最开始是有了 ncurses 之后,中文显示异常。这个是通过setlocale解决的。然后又是光标放的位置不对。于是又用上了我同样不熟悉的 wchar,自己计算光标应该放在哪里。
#define _XOPEN_SOURCE 700 /* for wcswidth and 700 is for mbsnrtowcs */
#include<wchar.h>
#include<ncurses.h> /* ncurses.h includes stdio.h */
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<readline/readline.h>
#include<locale.h>
int mygetstr(char *str, int y, int x){
WINDOW *win;
int size, col;
int ok = 0;
int width;
wchar_t wstr[80];
char *p;
getmaxyx(stdscr, size, col);
void getaline(char *s){
str = s;
rl_callback_handler_remove();
ok = 1;
}
rl_callback_handler_install("", getaline);
win = newwin(1, col-x, y, x);
while(1){
rl_callback_read_char();
if(ok)
break;
werase(win);
strncpy(str, rl_line_buffer, 80);
p = str;
/* how many column chars before cursor occupies? */
size = mbsnrtowcs(wstr, (const char**)&p, rl_point, 80, NULL);
width = wcswidth(wstr, size);
mvwprintw(win, 0, 0, "%s", str);
/* put the cursor at right column */
wmove(win, 0, width);
wrefresh(win);
}
delwin(win);
return 0;
}
int main(){
char mesg[] = "Enter a string: ";
char str[80];
int row, col;
setlocale(LC_ALL, ""); /* make ncurses handle Chinese correctly */
initscr();
getmaxyx(stdscr, row, col);
mvprintw(row / 2, (col - strlen(mesg)) / 2, "%s", mesg);
refresh();
mygetstr(str, row / 2, (col + strlen(mesg)) / 2);
mvprintw(LINES - 2, 0, "You Entered: %s", str);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
注意:此代码只是演示用,缓冲区溢出什么的我都没处理。
终于搞定了 C 下结合两者的使用,接下来 Python 版思路是有了,但因为其标准库 readline 中没有提供rl_callback_read_char()函数,所以只能用 ctypes 了。下面是在 Python 里使用rl_callback_read_char()的示例,ncurses 部分我暂时不想折腾了。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# vim:fileencoding=utf-8
import sys
import readline
import ctypes
import ctypes.util
rllib_path = ctypes.util.find_library('readline')
rllib = ctypes.CDLL(rllib_path)
def callback(s):
if s is None:
rllib.rl_callback_handler_remove()
sys.stdout.write('\n')
sys.exit()
elif not s:
pass
else:
print('%s.' % s.decode())
# 这样也可以
# print(readline.get_line_buffer())
cbfunc = ctypes.CFUNCTYPE(None, ctypes.c_char_p)
rllib.rl_callback_handler_install.restype = None
rllib.rl_callback_handler_install(ctypes.c_char_p(b">> "), cbfunc(callback))
while True:
rllib.rl_callback_read_char()
2011年8月4日更新:今天终于完成了个 quick and dirty 的 Python 版:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# vim:fileencoding=utf-8
import sys
import readline
import ctypes
import ctypes.util
import curses
import struct
from 字符集 import width
rllib_path = ctypes.util.find_library('readline')
rllib = ctypes.CDLL(rllib_path)
def getstr(win, y, x):
_, col = win.getmaxyx()
inputbox = curses.newwin(1, col-x, y, x)
ret = ''
ok = False
def callback(s):
nonlocal ok, ret
if s is None:
rllib.rl_callback_handler_remove()
raise EOFError
elif not s:
ok = True
else:
ret = s.decode()
ok = True
cbfunc = ctypes.CFUNCTYPE(None, ctypes.c_char_p)
rllib.rl_callback_handler_install.restype = None
rllib.rl_callback_handler_install(ctypes.c_char_p(b""), cbfunc(callback))
while True:
rllib.rl_callback_read_char()
if ok:
break
inputbox.erase()
# 这样获取的值不对。。。
# bbuf = ctypes.string_at(rllib.rl_line_buffer)
buf = readline.get_line_buffer()
bbuf = buf.encode()
inputbox.addstr(0, 0, buf)
rl_point = struct.unpack('I', ctypes.string_at(rllib.rl_point, 4))[0]
w = width(bbuf[:rl_point].decode())
inputbox.move(0, w)
inputbox.refresh()
del inputbox
return ret
msg = '输入字符串:'
win = curses.initscr()
curses.noecho()
row, col = win.getmaxyx()
win.addstr(row // 2, (col - width(msg)) // 2, msg)
win.refresh()
s = getstr(win, row // 2, (col + width(msg)) // 2)
win.addstr(row - 2, 0, '你输入了: ' + s)
win.getch()
curses.endwin()
26
2011
GM脚本:维基百科语言链接中,中英文优先
每次在一大堆语言列表中找“中文”或者“English”实在太累,所以想了这么个办法。虽然维基百科的页面已经使用了jQuery,但我还是执着地没有使用它。不过也用到了点新东西——XPath:
// ==UserScript==
// @name Wikipedia 语言链接顺序调整
// @description 将维基百科中的中英文语言链接放到最前面
// @namespace http://lilydjwg.is-programmer.com/
// @include http://*.wikipedia.org/*
// @include http://*.wiktionary.org/*
// @include https://*.wikipedia.org/*
// @include https://*.wiktionary.org/*
// ==/UserScript==
var links = document.evaluate('//*[@id="p-lang"]//a[text()="中文" or text()="English"]', document, null, XPathResult.UNORDERED_NODE_SNAPSHOT_TYPE, null);
var ul;
for(var i=0, len=links.snapshotLength; i<len; i++){
var link = links.snapshotItem(i);
ul = ul || link.parentNode.parentNode;
ul.insertBefore(link.parentNode, ul.firstChild);
}
我第一次、也是唯一一次看到在火狐中使用XPath的示例在这里。这里是MDC文档。
2011年8月12日更新:加入了维基词典的支持。
2011年11月7日更新:加入对 HTTPS 的支持。
1
2011
GM 脚本:Google顶栏还是白色的好看
月光都说了,Google的大多数页面还是白色顶栏比较合适,黑的看着实在是不爽。所以还是改回来好了:
// ==UserScript==
// @name White Google topbar
// @namespace http://lilydjwg.is-programmer.com/
// @description bring back google's white topbar
// @include http://*.google.com*
// @include https://*.google.com*
// ==/UserScript==
var css = "#gbx3, #gbx4 { background-color: #ffffff; border-bottom: 1px solid #3366cc; } #gbz .gbzt, #gbz .gbgt, #gbg .gbgt, .gbts, .gbz0l { color: #3366cc !important; } .gbzt-hvr, .gbzt:focus, .gbgt-hvr, .gbgt:focus { background-color: #eff3fb; } .gbz0l .gbtb2 { border-top-color: #3d7af5 !important; } #gbi5 { background-position: -6px -22px; }";
if (typeof GM_addStyle != "undefined") {
GM_addStyle(css);
} else if (typeof PRO_addStyle != "undefined") {
PRO_addStyle(css);
} else if (typeof addStyle != "undefined") {
addStyle(css);
} else {
var heads = document.getElementsByTagName("head");
if (heads.length > 0) {
var node = document.createElement("style");
node.type = "text/css";
node.appendChild(document.createTextNode(css));
heads[0].appendChild(node);
}
}
点击安装。
29
2011
使用 zsh 的 zpty 模块
Zsh 的模块真多呀,最初文档时知道有 ztcp 模块时已惊叹,最近又在邮件列表看到竟然有 zpty 模块,解决了困扰我良久的一个小问题。
会往终端输出彩色字符的程序都知道,如果输出的目的地不是终端,通常彩色转义字符是不需要的,比如重定向到文件,或者通过管道传给 grep 之类的程序。所以不少程序会有个--color=WHEN选项,你可以指定是程序自己决定,还是总是要彩色或者不要彩色。Linux 总是善于提供一堆选项来满足不同的需要。可是,除此之外,ls 还会根据输出目的地是不是终端来确定要不要一行显示多个文件名。更囧的是,只有办法强制 ls 一行显示一个文件名,却没有选项强制它把管道当成终端进行多栏显示。结果就是,当文件比较多时,ls | less会一行一个文件名,即使右边还有大把的空间。强制显示彩色也需要--color=always这么长的参数(而 tree 只需要-C就可以了)。
很早就想写个程序利用专门的伪终端来给 ls 的彩色多栏输出加上翻页器了。现在我终于把它实现了,而且简单很多:
ptyrun () {
local ptyname=pty-$$
zmodload zsh/zpty
zpty $ptyname ${1+"$@"}
if [[ ! -t 1 ]]; then
setopt local_traps
trap '' INT
fi
zpty -r $ptyname
zpty -d $ptyname
}
ptyless () {
ptyrun $@ | less
}
另外,这个用于 yaourt 查找时也是不错的 ;-)
2014年8月22日更新:采纳评论中的建议,使用管道取代了临时文件。另外,在 Dropbox 可以下载我的 zshrc。
